0 of 20 questions completed
Questions:
This diagnostic test is comprised of 20 items, which must be completed within 15 minutes.
Some items refer to the Periodic Table of Elements. To view the table while in an item screen, click the Exhibit button, located in the lower left corner of the screen. Each test item is a question or incomplete statement followed by suggested answers or completions. Read the item, decide which choice is best, and select the answer with the mouse. A navigation bar is provided, enabling you to skip between questions easily and mark questions for review. To unlock more practice tests and conquer the PCAT, upgrade here |
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Exam is loading ...
You must sign in or sign up to start the exam.
You have to finish following exam, to start this exam:
0 of 20 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You answered 0 of 0 (0) questions correct
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 200
Just know, when you truly want success, you’ll never give up on it. No matter how bad the situation may get. Keep your head up and keep on fighting!
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: Less than 350
Just know, when you truly want success, you’ll never give up on it. No matter how bad the situation may get. Keep your head up and keep on fighting!
Estimated PCAT General ChemistryScore: Less than 330
You’re on the right track. Take your time to reflect on your performance and how you can improve your scores the next time around. Carefully review these solutions, learn from your mistakes and understand the intricacies of each question. You’re going in the correct direction and you’ll only go up from here!
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 340
You’re on the right track. Take your time to reflect on your performance and how you can improve your scores the next time around. Carefully review these solutions, learn from your mistakes and understand the intricacies of each question. You’re going in the correct direction and you’ll only go up from here!
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 370
You’re on the right track. Take your time to reflect on your performance and how you can improve your scores the next time around. Carefully review these solutions, learn from your mistakes and understand the intricacies of each question. You’re going in the correct direction and you’ll only go up from here!
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 390
You’re doing a good job! Keep working on it and you’ll soon see your score in the 20’s. Take your time in understanding your mistakes and in carefully reviewing these solutions and learning from the intricacies of each question.
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 410
Good going! You are really getting to where you need to be. Keep it going! Take your time in understanding your mistakes and in carefully reviewing these solutions and understanding the intricacies of each question. Your goal should be to beat your 410 on the next test! Every point you get correct will get you closer to the perfect 600!
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 430
Good going! You are really getting to where you need to be. Keep it going! Keep on working on it and you’ll soon see your score in the 500’s. Take your time in understanding your mistakes and in carefully reviewing these solutions and understanding the intricacies of each question. Your goal should be to beat your 430 on the next test!
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 450
Awesome job! Keep it up and you’ll soon be in the 500’s. Learn from your mistakes and strategize on how you’ll beat your 450!
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 470
Awesome job! You did it! You really outdid yourself today. What can we do differently on the next exam to get yourself up to 500? Lets do it!
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 500
Impressive! You hit 500! Now let’s push you up to the perfect 600!
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 540
You rocked it! That was quite an accomplishment!
Estimated PCAT General Chemistry Score: 570 or higher
You are a rockstar! We tip our hats to you!
1. The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/gK. Calculate the final temperature of the mixture when 50.0 g of water at 358K is added to 100.0 g of water at 298K.
When dealing with specific heat, we use the following equation:
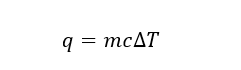
where m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat of the substance, and ΔT is the temperature change. Here we are adding two different samples of water. One is a 50g sample at 358K, and the other is a 100g sample at 298K. The one at the higher temperature will lose heat, while the other at the lower temperature will gain heat upon mixing. As a result, the final temperature will be somewhere between 358K and 298K.
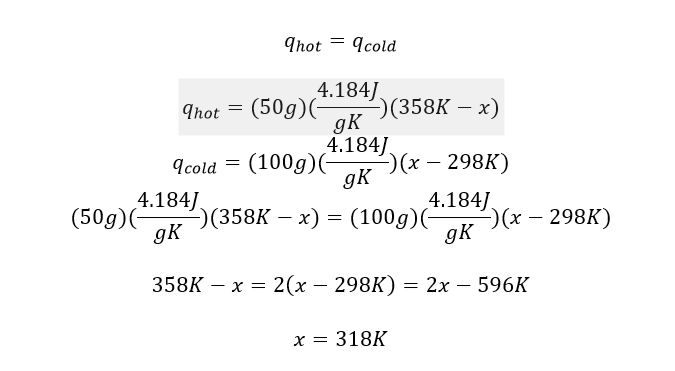
When dealing with specific heat, we use the following equation:
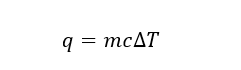
where m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat of the substance, and ΔT is the temperature change. Here we are adding two different samples of water. One is a 50g sample at 358K, and the other is a 100g sample at 298K. The one at the higher temperature will lose heat, while the other at the lower temperature will gain heat upon mixing. As a result, the final temperature will be somewhere between 358K and 298K.
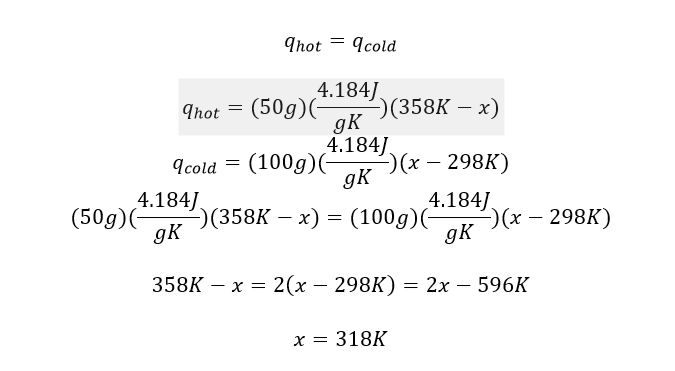

2.The compound with the formula NH4NO2 is named
NH4+ is called ammonium and NO2– is called nitrite. The two molecular ions together form ammonium nitrite.
NH4+ is called ammonium and NO2– is called nitrite. The two molecular ions together form ammonium nitrite.

3.
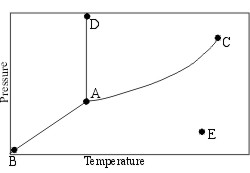
Which line distinguishes a liquid from a gas?
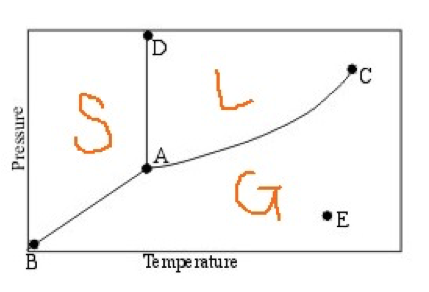
The region labeled L is where the substance exists in the liquid state, and the one labeled G is where it exists in the gas (vapor) state. Therefore, the line AC distinguishes the liquid state from the gas state.

The region labeled L is where the substance exists in the liquid state, and the one labeled G is where it exists in the gas (vapor) state. Therefore, the line AC distinguishes the liquid state from the gas state.

4. The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in the n = 3 shell is
In the n=3 shell, the possible subshells are the s, p, and d subshells. The s subshell can hold 2 electrons, while the p subshell can hold 6, and the d subshell, 10. The total is 18. Therefore, the correct answer is Choice D.
In the n=3 shell, the possible subshells are the s, p, and d subshells. The s subshell can hold 2 electrons, while the p subshell can hold 6, and the d subshell, 10. The total is 18. Therefore, the correct answer is Choice D.

5. The quantum of light energy is the
A photon is the quantum of light, and thus Choice D is correct. A neuron is a nerve cell, and an exciton is a bound state of an electron. As you already know, an electron is a subatomic particle with a negative charge. A phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic arrangement of atoms or molecules in a condensed matter.
A photon is the quantum of light, and thus Choice D is correct. A neuron is a nerve cell, and an exciton is a bound state of an electron. As you already know, an electron is a subatomic particle with a negative charge. A phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic arrangement of atoms or molecules in a condensed matter.

6. Which of the following led to Einstein’s quantization of the energy of light?
Light energy being carried in discrete quantized packets (quantum) is due to the photoelectric effect. Choice B is clearly the answer.
Light energy being carried in discrete quantized packets (quantum) is due to the photoelectric effect. Choice B is clearly the answer.

7. The first law of thermodynamics states the following
The first law of thermodynamics states that the energy of an isolated system is constant. It also states that energy can be transformed from one form to another, but never destroyed or created. Choice C correctly describes this.
The first law of thermodynamics states that the energy of an isolated system is constant. It also states that energy can be transformed from one form to another, but never destroyed or created. Choice C correctly describes this.

8. Which of these statements concerning solubility is NOT true?
In order to answer this question, you need to be familiar with the solubility rules:
Rule 1. All compounds of Group IA elements (the alkali metals) are soluble.
Rule 2. All ammonium salts (salts of NH4+) are soluble.
Rule 3. All nitrate (NO3–), chlorate (ClO3–), perchlorate (ClO4–), and acetate (CH3COO–) salts are soluble.
Rule 4. All chloride (Cl–), bromide (Br–), and iodide (I–) salts are soluble except for those of Ag+, Pb2+, and Hg22+.
Rule 5. All sulfate ( SO42-) compounds are soluble except those of Ba2+, Sr2+, Ca2+, Pb2+, Hg22+, and Hg2+, Ca2+ and Ag+ sulfates are only moderately soluble.
Rule 6. All hydroxide (OH–) compounds are insoluble except those of Group I-A (alkali metals) and Ba2+, Ca2+, and Sr2+.
Rule 7. All sulfide (S2-) compounds are insoluble except those of Groups I-A and II-A (alkali metals and alkali earths).
Rule 8. All sulfites (SO3–), carbonates (CO32-), chromates (CrO42-), and phosphates (PO43-) are insoluble except for those of NH4+ and Group I-A (alkali metals)(see rules 1 and 2).
Choice D is an incorrect statement because not all halides are soluble. See Rule 4 provided above.
In order to answer this question, you need to be familiar with the solubility rules:
Rule 1. All compounds of Group IA elements (the alkali metals) are soluble.
Rule 2. All ammonium salts (salts of NH4+) are soluble.
Rule 3. All nitrate (NO3–), chlorate (ClO3–), perchlorate (ClO4–), and acetate (CH3COO–) salts are soluble.
Rule 4. All chloride (Cl–), bromide (Br–), and iodide (I–) salts are soluble except for those of Ag+, Pb2+, and Hg22+.
Rule 5. All sulfate ( SO42-) compounds are soluble except those of Ba2+, Sr2+, Ca2+, Pb2+, Hg22+, and Hg2+, Ca2+ and Ag+ sulfates are only moderately soluble.
Rule 6. All hydroxide (OH–) compounds are insoluble except those of Group I-A (alkali metals) and Ba2+, Ca2+, and Sr2+.
Rule 7. All sulfide (S2-) compounds are insoluble except those of Groups I-A and II-A (alkali metals and alkali earths).
Rule 8. All sulfites (SO3–), carbonates (CO32-), chromates (CrO42-), and phosphates (PO43-) are insoluble except for those of NH4+ and Group I-A (alkali metals)(see rules 1 and 2).
Choice D is an incorrect statement because not all halides are soluble. See Rule 4 provided above.

9. The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. How many electrons exist in the valence shell of a single uncharged nitrogen atom?
Nitrogen is in the second period, and it has 5 valence electrons. Therefore, Choice E is correct.
Nitrogen is in the second period, and it has 5 valence electrons. Therefore, Choice E is correct.

10. Balance the following equation. C2H6 + O2 -> CO2 + H2O
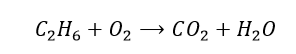
Compare the number of atoms of each element on both sides. We have 6 hydrogen atoms on the reactants side, but there are only 2 on the products side. Let’s multiply the water term by 3 and see what happens.
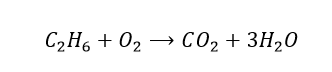
Now, there are 2 carbon atoms on the left-hand side, but there is only 1 on the right-hand side. So we will multiply the carbon dioxide term by 2.
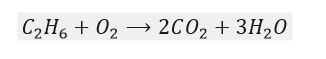
So now we must focus on the number of oxygen atoms. On the reactant side, there are only 2 oxygen atoms, whereas on the product side, there are 7. By multiplying the O2 term by 3.5, we should have a balanced equation, right?
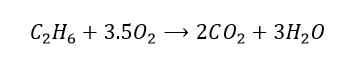
But we are not quite there just yet… we want the coefficients to be whole numbers. Therefore,
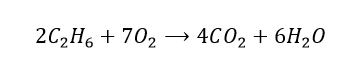
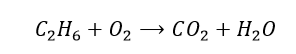
Compare the number of atoms of each element on both sides. We have 6 hydrogen atoms on the reactants side, but there are only 2 on the products side. Let’s multiply the water term by 3 and see what happens.
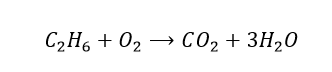
Now, there are 2 carbon atoms on the left-hand side, but there is only 1 on the right-hand side. So we will multiply the carbon dioxide term by 2.
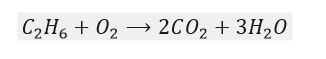
So now we must focus on the number of oxygen atoms. On the reactant side, there are only 2 oxygen atoms, whereas on the product side, there are 7. By multiplying the O2 term by 3.5, we should have a balanced equation, right?
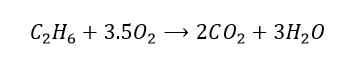
But we are not quite there just yet… we want the coefficients to be whole numbers. Therefore,
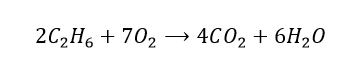

11.
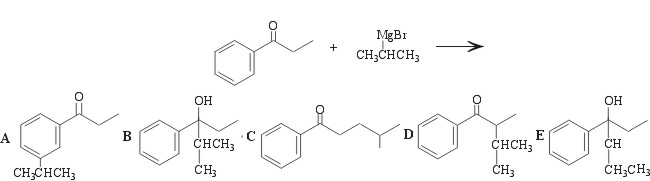
We are given a carbonyl compound and a Grignard reagent. The Grignard reagent will attack the carbonyl carbon in the presence of dry ether, and a new carbon-carbon bond will form. Upon an acid workup, the carbonyl group will be completely reduced to a hydroxyl group.
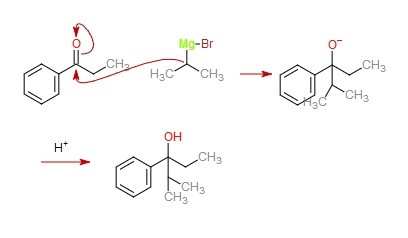
We are given a carbonyl compound and a Grignard reagent. The Grignard reagent will attack the carbonyl carbon in the presence of dry ether, and a new carbon-carbon bond will form. Upon an acid workup, the carbonyl group will be completely reduced to a hydroxyl group.


12.
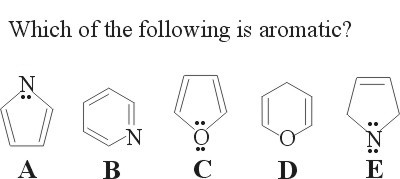
Aromatic compounds have:
Both Choices B and C are aromatic compounds.
Aromatic compounds have:
Both Choices B and C are aromatic compounds.

13.
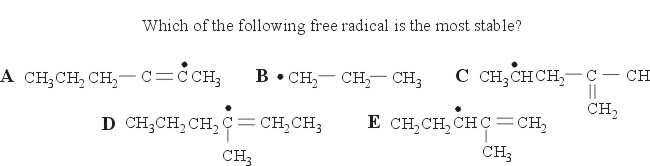
The stability of free radicals is much like that of carbocations. The higher the degree of alkyl substitution, the greater the stability. Choice A is a vinyl free radical, which is very unstable. Choice B is a primary radical, while Choice C is secondary. Also, Choice D is not a radical (count the number of the bonds on the carbon atom bearing the free radical). Finally, Choice E is an allylic free radical, which is very stable due to the resonance created. Therefore, Choice E is the correct answer.
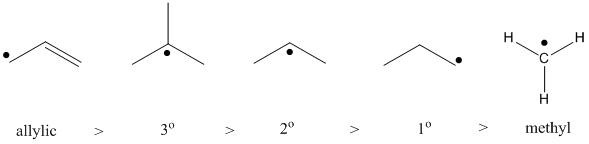
The stability of free radicals is much like that of carbocations. The higher the degree of alkyl substitution, the greater the stability. Choice A is a vinyl free radical, which is very unstable. Choice B is a primary radical, while Choice C is secondary. Also, Choice D is not a radical (count the number of the bonds on the carbon atom bearing the free radical). Finally, Choice E is an allylic free radical, which is very stable due to the resonance created. Therefore, Choice E is the correct answer.


14. An amino acid at its isoelectric point has an overall charge of?
The isoelectric point, pI, is the pH at which the amino acids are neutral. In other words, at its pI, an amino acid has an overall charge of 0. Choice C is the answer.
The isoelectric point, pI, is the pH at which the amino acids are neutral. In other words, at its pI, an amino acid has an overall charge of 0. Choice C is the answer.

15.
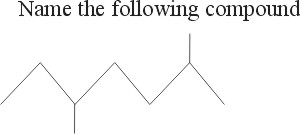
When naming a compound, first find the longest parent chain. Then, number the substituents with the lowest numbers possible. In this structure, the parent chain is 7 carbon long. Then there are two methyl groups attached at the 2 and 5 positions. Therefore, the name of this compound is 2,5-dimethylheptane.
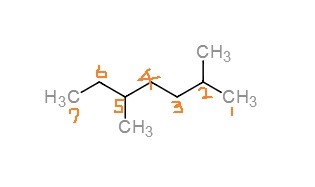
When naming a compound, first find the longest parent chain. Then, number the substituents with the lowest numbers possible. In this structure, the parent chain is 7 carbon long. Then there are two methyl groups attached at the 2 and 5 positions. Therefore, the name of this compound is 2,5-dimethylheptane.


16.
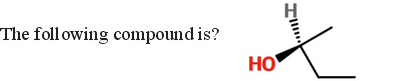
Because the chiral carbon atom is connected to 4 different groups, you should notice that the configuration will be either R or S. Among the four groups, the oxygen atom of the hydroxyl (alcohol) group has the highest atomic number, and thus has the highest priority. The ethyl group comes second, followed by the methyl group. Lastly, the hydrogen atom has the lowest priority. Since the direction is counterclockwise, and the lowest priority group is on a dash, the configuration is S.
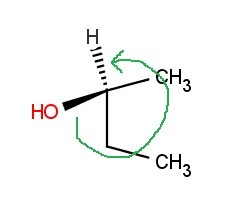
Because the chiral carbon atom is connected to 4 different groups, you should notice that the configuration will be either R or S. Among the four groups, the oxygen atom of the hydroxyl (alcohol) group has the highest atomic number, and thus has the highest priority. The ethyl group comes second, followed by the methyl group. Lastly, the hydrogen atom has the lowest priority. Since the direction is counterclockwise, and the lowest priority group is on a dash, the configuration is S.


17.
Because the chiral carbon atom is connected to 4 different groups, you should notice that the configuration will be either R or S. Among the four groups, the oxygen atom of the hydroxyl (alcohol) group has the highest atomic number, and thus has the highest priority. The ethyl group comes second, followed by the methyl group. Lastly, the hydrogen atom has the lowest priority. Since the direction is counterclockwise, and the lowest priority group is on a dash, the configuration is S.
Because the chiral carbon atom is connected to 4 different groups, you should notice that the configuration will be either R or S. Among the four groups, the oxygen atom of the hydroxyl (alcohol) group has the highest atomic number, and thus has the highest priority. The ethyl group comes second, followed by the methyl group. Lastly, the hydrogen atom has the lowest priority. Since the direction is counterclockwise, and the lowest priority group is on a dash, the configuration is S.

18.
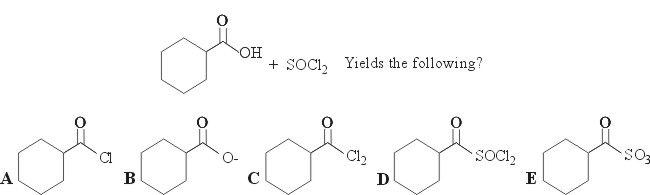
Acyl chlorides can be prepared by reacting a carboxylic acid with thionyl chloride (SOCl2). The –OH group is simply replaced by –Cl, and the resulting acyl chlorides are very reactive species. Choice A is the correct answer.
Acyl chlorides can be prepared by reacting a carboxylic acid with thionyl chloride (SOCl2). The –OH group is simply replaced by –Cl, and the resulting acyl chlorides are very reactive species. Choice A is the correct answer.

19.
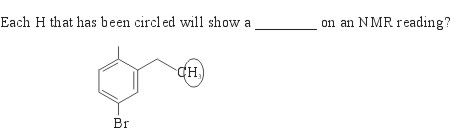
In the diagram, the carbon to which the three hydrogen atoms are attached is in turn attached to a carbon that is attached to two hydrogens. These two hydrogens will cause the three hydrogens to show a triplet on the 1H NMR signals. On the other hand, the three hydrogens will cause the two hydrogens to give rise to a quartet as its 1H NMR signal. Choice C is correct.
In the diagram, the carbon to which the three hydrogen atoms are attached is in turn attached to a carbon that is attached to two hydrogens. These two hydrogens will cause the three hydrogens to show a triplet on the 1H NMR signals. On the other hand, the three hydrogens will cause the two hydrogens to give rise to a quartet as its 1H NMR signal. Choice C is correct.

20. As monosaccharides change from a straight chain to a cyclic form, they can become
When monosaccharides change from a straight chain to a cyclic form, they can become hemiketals or hemiacetals depending on their types. If a monosaccharide is a ketose, it becomes a hemiketal; if it is an aldose, it becomes a hemiacetal.
When monosaccharides change from a straight chain to a cyclic form, they can become hemiketals or hemiacetals depending on their types. If a monosaccharide is a ketose, it becomes a hemiketal; if it is an aldose, it becomes a hemiacetal.


